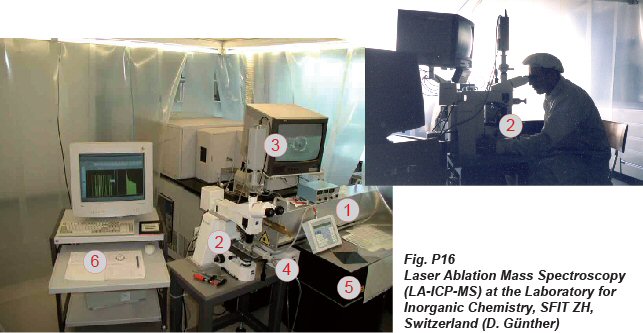
Explanation
of method.
The laser ablation technique (LA) uses a 193
nm excimer laser (1) which is focused onto the
sample surface via microscope lenses (2). The
laser is ablating (carrying away) the material
(crater diameter 4 to 80 microns) (3). The mobilized
material is suspended in a carrier gas (4) and
transported via transport tube into an Inductively
Coupled Plasma Mass Spectrometer (ICP-MS) (5).
The material/elements (except those that cannot
be ionized, such as gases and fluorine) are
vaporized, atomized and ionized within the ICP
. The created ions are then transferred to the
mass spectrometer and separated by their mass
divided by charge (5). The detector allows measuring
major, minor and trace elements within a single
analysis. Very light elements, such as boron,
lithium or beryllium, can be detected, along
with a large series of other elements at concentrations
of less then 1 ppm. The quantification at low
concentrations is possible by LA-ICP-MS due
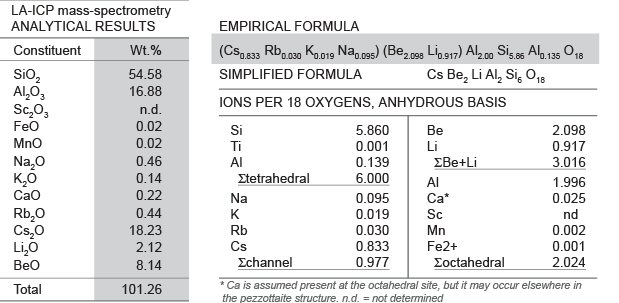
to a matrix-independent calibration, e.g. glass
standard was used for quantification of pezzottaite
including special computer analysis and specific
software (6). The use of complementary solid-analysis
methods (such as EMPA and XRF) for comparison
and validation purposes (e.g. for quantitative
measurement of silicon and aluminium) must be
applied (see Box 4A).


No.3 August 2004 |
|||||||||||||||||||
 |
What 's inside? - Cover Page - Forward - Editor and Editional Review Board |
||||||||||||||||||
|
|||||||||||||||||||